Ultrasound has become one of the most valuable tools in modern cattle reproduction management. Whether you are managing a small family-run operation or a large-scale beef or dairy enterprise, using ultrasound to diagnose pregnancy in cows can improve efficiency, reduce costs, and optimize herd health. ในบทความนี้, we’ll walk through everything you need to know about how to perform cattle pregnancy checks with ultrasound, including when to do it, what equipment is needed, how to interpret results, and best practices for safety and accuracy.

Section 1: Why Use Ultrasound for Pregnancy Detection in Cattle?
Traditional methods of pregnancy diagnosis in cattle include rectal palpation and observation of behavioral signs, but these approaches have limitations in accuracy and timing. Ultrasound, or ultrasonography, offers several advantages:
-
Early Detection: Pregnancy can be confirmed as early as 28 days post-breeding.
-
Fetal Viability: You can check for a heartbeat and assess whether the embryo is developing normally.
-
Fetal Sexing: From around 55 ถึง 70 days of gestation, fetal gender can often be determined.
-
Twin Detection: Identifying twins early helps in nutritional and management adjustments.
-
Accurate Records: Ultrasound gives visual evidence, which is easier to document and track.
Section 2: Equipment You Will Need
To perform ultrasound on cattle, you’ll need the following:
-
เครื่องอัลตราซาวนด์สัตวแพทย์: Preferably a portable unit designed for large animals, with a rectal probe. Linear and convex rectal probes are common.
-
Probe Sleeve or Glove: Long, disposable sleeves to maintain hygiene.
-
Ultrasound Gel: Enhances image quality by ensuring good contact between the probe and tissues.
-
Restraint Equipment: Cattle chute or head gate to safely restrain the animal during the procedure.

Tip: When purchasing an เครื่องอัลตราซาวนด์, look for units that are rugged, กันน้ํา, and offer clear grayscale imaging. Battery-powered models with a long operating time are ideal for field use.
Section 3: When and How to Perform the Ultrasound
Timing is critical for accurate pregnancy diagnosis. The ideal window for ultrasound pregnancy checks in cattle is between 28 และ 90 วันหลังการผสมเทียม. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to perform the procedure:
-
Restrain the Cow Use a squeeze chute or cattle head gate to safely restrain the cow. A well-lit and clean working area will reduce stress and improve safety.
-
Prepare the Equipment Attach the probe to the เครื่องอัลตราซาวนด์, apply ultrasound gel to the probe tip, and wear a long plastic sleeve over your arm for sanitation.
-
Insertion and Scanning Gently insert your hand with the probe into the rectum of the cow. Guide the probe downward toward the uterus. Move slowly and scan systematically to locate the uterine horns. At around 30–35 days, a fluid-filled vesicle with an embryo can usually be identified.
-
Interpreting the Image Once the pregnancy is confirmed, assess the fetus for:
-
Heartbeat (visible by day 25–30)
-
Placental attachment
-
Embryonic shape and size
-
Signs of twin embryos (check both uterine horns)
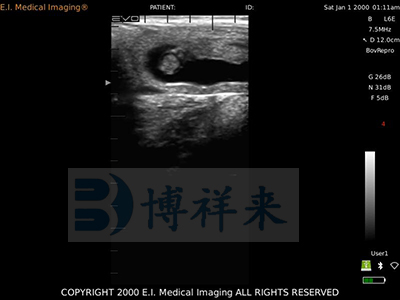
Cow gestation period 34 วัน
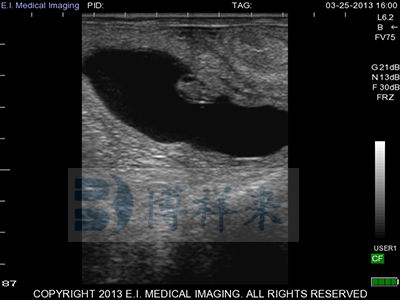
Cow gestation period 35 วัน
Section 4: Fetal Sexing and Twin Diagnosis
Fetal sexing is typically performed between 55 และ 70 days of gestation. This requires high-resolution imaging and skill in identifying genital tubercle location—closer to the umbilicus in males and near the tail in females.
Twin pregnancies are more common in dairy breeds like Holsteins and can be detected early with ultrasound. It’s important to monitor these pregnancies closely, as they are associated with higher risks of abortion and dystocia.
Section 5: Safety Considerations
ขณะ ultrasound is non-invasive and safe for both the cow and operator, proper hygiene and care should always be taken:
-
Clean the equipment thoroughly between animals to prevent disease transmission.
-
Use plenty of ultrasound gel to reduce friction.
-
Avoid excessive pressure that could harm the fetus or cause discomfort to the cow.
-
Ensure the cow is calm before and during the procedure—stress can affect results and safety.
Section 6: Recording and Follow-Up
After each scan, record the following data:
-
Cow identification number
-
Date of insemination or breeding
-
Pregnancy status (pregnant/open)
-
Estimated gestational age
-
Notes on fetal viability, sex (if known), or presence of twins
Follow-up checks may be necessary for cows showing ambiguous results or those with high-risk pregnancies. For open cows, prompt resynchronization and breeding can minimize lost reproductive time.
Section 7: Training and Skill Development
Although experienced veterinarians and technicians can perform ultrasounds with precision, many producers now learn to conduct their own scans. Online courses, workshops, and practice on known-pregnant cows are excellent ways to gain confidence. Keep in mind:
-
Image interpretation takes practice.
-
It’s better to scan later (e.g., 35–40 days) during early learning stages for easier detection.
-
Maintain regular communication with your vet for guidance and backup when needed.
Section 8: Economic Benefits
Using ultrasound for pregnancy diagnosis provides several economic advantages:
-
Shortened calving intervals by quickly identifying open cows
-
Reduced feed costs by culling or isolating non-pregnant cows earlier
-
Improved reproductive performance through better data management
-
Enhanced animal welfare by avoiding unnecessary hormonal treatments or rebreeding efforts
บทสรุป
Ultrasounding cattle for pregnancy is a game-changer for reproductive management ในฟาร์ม. With the right equipment, proper technique, and a little training, you can gain precise insights into your herd’s reproductive status. Whether you’re raising beef or dairy cattle, using ultrasound to detect pregnancy early helps make informed decisions, improving productivity and profitability across the board.
Take the time to invest in this powerful technology—your herd and your bottom line will thank you.