Imágenes de ultrasonido, o ecografía, es una piedra angular del diagnóstico veterinario, ofreciendo un sistema no invasivo, Visión en tiempo real de las estructuras internas de los animales. Aprovechando las ondas sonoras de alta frecuencia, this technology enables veterinarians to assess organs, tissues, and blood flow without the need for surgery or exposure to ionizing radiation.
The Science Behind Ultrasound Imaging
At the heart of ultrasound technology lies the transducer, a device that emits and receives sound waves. When placed against the animal’s body, often with the aid of a conductive gel, the transducer sends out high-frequency sound waves that penetrate the tissues. As these waves encounter different structures within the body, they are reflected back to the transducer at varying degrees, depending on the density and composition of the tissues. These returning echoes are then converted into electrical signals, which are processed to create visual images on a monitor.
The frequency of the sound waves, Por lo general, van desde 1 Para 22 megahertz (MHz), plays a crucial role in image quality. Higher frequencies provide better resolution but have limited penetration depth, making them ideal for imaging superficial structures like tendons and eyes. Lower frequencies penetrate deeper but offer lower resolution, suitable for examining organs such as the liver or heart .
B-Mode Grayscale Imaging: The Standard Approach
The most commonly used ultrasound imaging mode in veterinary practice is B-mode (brightness mode) grayscale imaging. This technique produces two-dimensional cross-sectional images, allowing for detailed visualization of internal structures. The varying shades of gray in the images correspond to the echogenicity of tissues:
-
Anechoic (Black): Fluids like urine or blood appear black due to the absence of echoes.
-
Hypoechoic (Dark Gray): Less dense tissues, such as certain organs, reflect fewer sound waves.
-
Hyperechoic (Bright): Dense structures like bones or fibrous tissues reflect more sound waves, appearing brighter on the image .
Understanding these variations is essential for accurate interpretation and diagnosis.
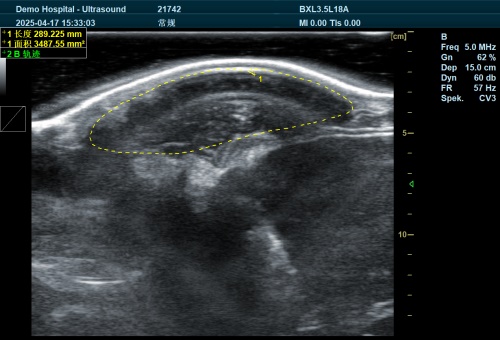
Interpreting Echogenicity and Tissue Characteristics
Echogenicity refers to the ability of tissues to reflect ultrasound waves. Changes in echogenicity can indicate various pathological conditions:
-
Increased Echogenicity: May suggest fibrosis, mineralization, or fat infiltration.
-
Decreased Echogenicity: Could indicate edema, inflamación, or cystic formations.
Por ejemplo, a liver with diffuse hyperechogenicity might be indicative of fatty infiltration, while a hypoechoic mass in the spleen could suggest a hematoma or neoplasia .
Recognizing and Understanding Artifacts
Artifacts are misleading features that appear on ultrasound images due to the interaction of sound waves with tissues. Common artifacts include:
-
Reverberation: Multiple reflections between two strong reflectors, creating parallel lines.
-
Shadowing: Occurs when sound waves are blocked by a dense object, resulting in a dark area beyond it.
-
Enhancement: Increased brightness beneath fluid-filled structures due to the lack of attenuation.
Being able to identify and interpret these artifacts is crucial to avoid misdiagnosis .
Advanced Ultrasound Modalities
Beyond B-mode imaging, several advanced ultrasound techniques enhance diagnostic capabilities:
-
Ecografía Doppler: Assesses blood flow within vessels, detecting abnormalities like blockages or turbulent flow.
-
Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound: Involves the use of microbubble contrast agents to improve visualization of blood flow and tissue vascularity .
-
Elastografía: Measures tissue stiffness, aiding in the differentiation of benign and malignant masses.
These modalities provide additional layers of information, facilitating more comprehensive evaluations.
Clinical Applications in Veterinary Medicine
Ultrasound is invaluable across various veterinary disciplines:
-
Imágenes abdominales: Evaluates organs such as the liver, riñones, and intestines for structural abnormalities.
-
Cardiac Assessment: Echocardiography examines heart function and detects conditions like valve disorders or cardiomyopathies.
-
Seguimiento reproductivo: Assists in Diagnóstico del embarazo and monitoring fetal development.
-
Musculoskeletal Evaluation: Identifies tendon injuries, joint effusions, and soft tissue masses.
Its versatility makes ultrasound an essential tool in both routine check-ups and emergency situations.
Limitations and Considerations
While ultrasound offers numerous advantages, it has limitations:
-
Operator Dependency: Image quality and interpretation heavily rely on the operator’s skill and experience.
-
Limited Penetration: High-frequency probes may not adequately image deep structures in large animals.
-
Obstruction by Gas or Bone: Air-filled or bony structures can hinder sound wave transmission, obscuring underlying tissues.
Understanding these constraints ensures appropriate use and interpretation of ultrasound findings.
Conclusión
Ultrasound imaging stands as a pivotal diagnostic tool in veterinary medicine, offering real-time, non-invasive insights into animal health. Its ability to visualize soft tissues, assess organ function, and guide clinical decisions underscores its value in modern veterinary practice.
References:
-
Merck Veterinary Manual – Ultrasonography in Animals: https://www.merckvetmanual.com/clinical-pathology-and-procedures/diagnostic-imaging/ultrasonography-in-animals
-
Today’s Veterinary Practice – Basics of Ultrasound Transducers and Image Formation: https://todaysveterinarypractice.com/radiology-imaging/physical-principles-of-abdominal-ultrasonography-part-1-basics-of-ultrasound-transducers-image-formation-2/
-
Antech Diagnostics – How Does Veterinary Ultrasound Work?: https://www.antechdiagnostics.com/equipment-resources/how-does-veterinary-ultrasound-work/
-
DVM360 – A Veterinary Technician’s Guide to Emergency Ultrasounds: https://www.dvm360.com/view/veterinary-technicians-guide-emergency-ultrasounds
-
Today’s Veterinary Practice – Physical Principles of Artifacts and False Assumptions: https://todaysveterinarypractice.com/radiology-imaging/imaging-essentialssmall-animal-abdominal-ultrasonography-part-2-physical-principles-artifacts-false-assumptions/