Ultrasound imaging is an essential tool in modern veterinary medicine. Whether you are diagnosing a cow’s pregnancy, checking a horse’s tendon, or evaluating the internal organs of a camel, having the right ultrasound probe is crucial. Different animals, body sizes, and diagnostic needs require specific types of probes to ensure accurate results.

소
이 기사에서, we’ll explore the major types of ultrasound probes used in veterinary practice, their structures, applications, and key considerations when choosing the right probe for different animals like cattle, 돼지, 말, 양, and camels.
1. Linear Probes
Structure and Features:
Linear probes have a straight, flat surface and produce high-frequency ultrasound waves, typically between 5 MHz and 15 메가 헤르츠. The beam travels straight down from the surface, making them ideal for imaging shallow structures.
Applications in Veterinary Medicine:
-
Equine Practice: Linear probes are often used to examine tendons and ligaments in horses’ limbs due to their excellent resolution at shallow depths.
-
Small Ruminants: Sheep and goats benefit from linear probes when scanning superficial organs like testes or small joints.
-
Swine: Used in early-stage pregnancy diagnosis because pig fetuses are relatively shallow at first.
Advantages:
-
High resolution
-
Excellent detail for superficial tissues
Limitations:
-
Poor penetration depth; not ideal for large animals’ deep organs
2. Convex (Curvilinear) Probes
Structure and Features:
Convex probes have a curved surface that produces a wider field of view. Their frequencies generally range between 2.5 MHz and 7.5 메가 헤르츠, offering a good balance between penetration and resolution.
Applications in Veterinary Medicine:
-
Cattle and Horses: Ideal for abdominal and thoracic examinations where deeper penetration is needed.
-
Camels: Given their size and body structure, convex probes are often used for reproductive and abdominal scans.
-
Pigs: Suitable for mid-to-late pregnancy diagnosis as fetuses grow deeper inside the uterus.
Advantages:
-
Good penetration for deep structures
-
Wide field of view
Limitations:
-
Slightly lower resolution compared to linear probes
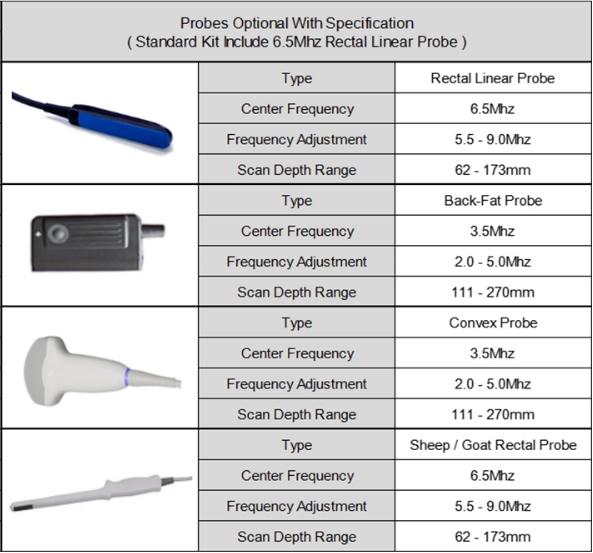
Types of Veterinary Ultrasound Probes
3. Microconvex Probes
Structure and Features:
These probes are similar to convex probes but with a smaller footprint, making them easier to handle around tight spaces and smaller animals. Frequencies are typically between 5 MHz and 8 메가 헤르츠.
Applications in Veterinary Medicine:
-
Small Animals: Dogs, 고양이, and newborn farm animals are commonly scanned with microconvex probes.
-
Neonatal Livestock: Perfect for examining calves, piglets, and lambs’ abdominal organs.
Advantages:
-
Better access to small or awkward anatomical regions
-
Decent balance of resolution and penetration
Limitations:
-
Slightly narrower field of view than standard convex probes
4. Phased Array Probes
Structure and Features:
Phased array probes have a small footprint and are designed to steer the ultrasound beam electronically. They generally operate at lower frequencies, 보낸 사람 1 MHz to 5 메가 헤르츠, enabling deep penetration.
Applications in Veterinary Medicine:
-
Large Animal Cardiology: Perfect for heart examinations in cattle and horses, especially for adult animals with thick chest walls.
-
Thoracic Scanning: Useful in diagnosing lung conditions or pleural effusion in large species.
Advantages:
-
Deep penetration
-
Small contact area, good for accessing between ribs
Limitations:
-
Lower image resolution
-
Steeper learning curve for image interpretation
5. Rectal Probes
Structure and Features:
Rectal probes are long, slim, and usually linear in design. They operate at higher frequencies (typically 5–8 MHz) for reproductive scanning through the rectal wall.
Applications in Veterinary Medicine:
-
Bovine Reproduction: Essential for pregnancy diagnosis and ovarian assessments in dairy and beef cattle.
-
Equine Reproduction: Used for checking mares for pregnancy or reproductive tract health.
-
Camelid Practice: Important in breeding management for camels and llamas.
Advantages:
-
Precise reproductive imaging
-
Easy access to reproductive organs
Limitations:
-
Limited to rectal examinations
-
Requires proper restraint and operator experience
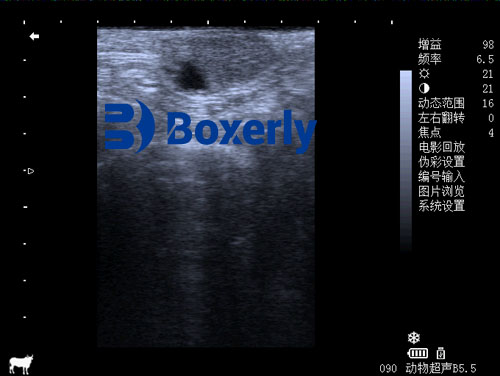
Bovine Corpus Luteum Ultrasound Imaging
How to Choose the Right Probe?
Choosing the correct probe depends on several factors:
-
Animal Species and Size: Larger animals require lower-frequency probes for better penetration, while smaller animals benefit from higher-frequency probes for better resolution.
-
Target Organ: Shallow structures (like tendons or superficial masses) need high-frequency probes, while deep organs (like the liver, 자궁, or heart) need lower-frequency probes.
-
Operator Experience: Some probes, like phased arrays, require more skill to use effectively.
-
Portability and Durability: In farm settings, a durable, portable ultrasound system with rugged probes is essential.
결론
Understanding the different types of ultrasound probes is vital for anyone involved in veterinary care, whether you’re a farm owner checking cow pregnancies, a veterinarian examining a racehorse, 또는 livestock breeder managing reproductive programs. Each probe type serves a specific purpose, and selecting the right one ensures the best possible diagnostic results.
When investing in veterinary ultrasound equipment, it’s crucial not only to focus on the machine itself but also on having the right probes on hand to match the diverse needs of your animals. A properly chosen probe can make all the difference between a vague image and a precise diagnosis.